Lexical Analysis is the first phase of the compiler. It converts the source code into tokens, which are the smallest meaningful units of the code. The program responsible for this is called a Lexical Analyzer or Lexer.
Example Program
int main() {
int a = 5, b = 3;
int sum = a + b;
printf("Sum is: %d", sum);
return 0;
}
1. Input to the Lexical Analyzer
The source code is provided to the Lexical Analyzer.
2. Breaking into Tokens
The Lexical Analyzer scans the code and breaks it into tokens:
- Keywords: int, return
- Identifiers: main, a, b, sum
- Operators: =, +
- Punctuation: (, ), {, }, ,, ;
- Literals: 5, 3
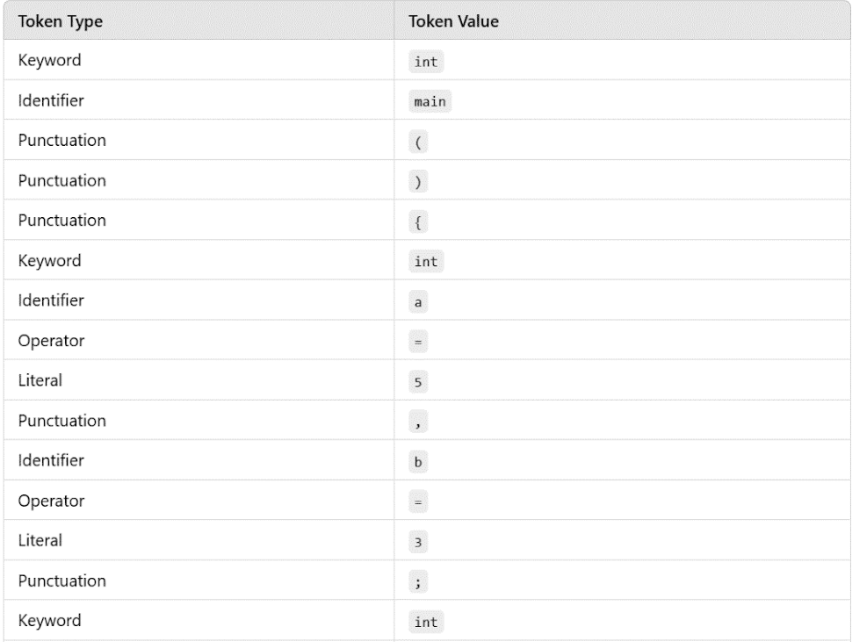
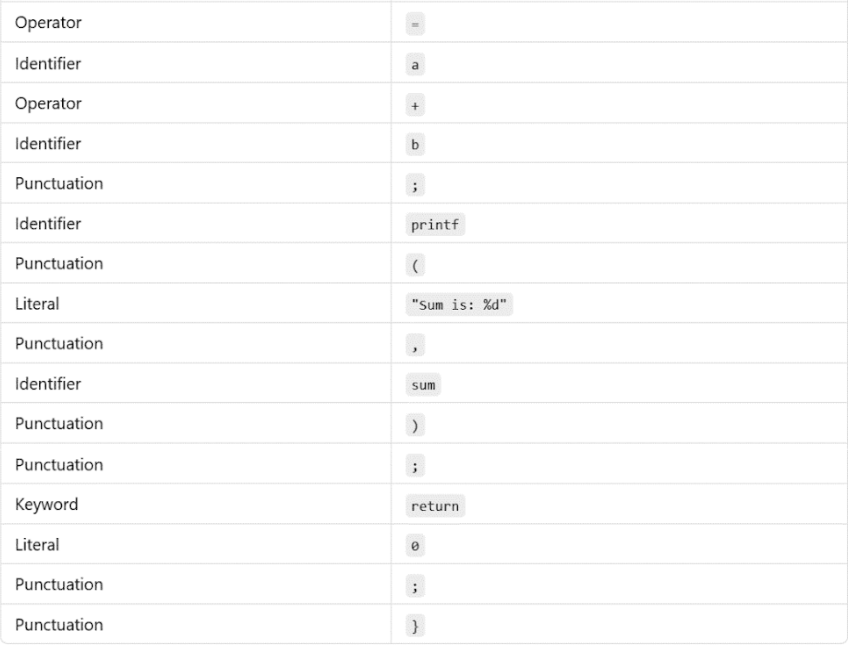
3. Output of the Lexical Analyzer
The output is a stream of tokens, like this:
Error Detection
During Lexical Analysis, the Lexer also detects lexical errors, such as:
- Invalid characters (e.g., @ in the code).
- Invalid identifiers (e.g., starting a variable name with a number, like 1var).
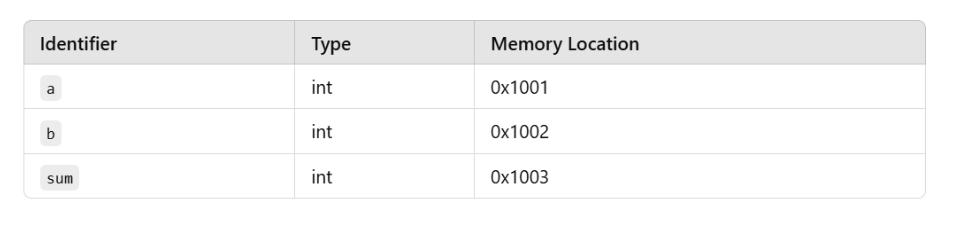
Symbol Table
The Lexer creates a symbol table that stores identifiers and their details (e.g., name, type, memory location).
Example for the above program: